How Oko Works
The Problem with Traditional Wallets
Traditional cryptocurrency wallets store a single private key that controls all user funds. This creates a fundamental security vulnerability:
- Lost key = lost funds (no recovery)
- Stolen key = stolen funds (no protection)
- Complex backup (seed phrases, hardware devices)
- Single point of failure (one vulnerability compromises everything)
Oko's Solution: Multi-Party Computation
Instead of one private key, Oko uses a 2-of-2 multi-party computation signing model that distributes cryptographic control across multiple parties. No single entity can access user funds.
How It Works
Traditional Wallet:
[Single Private Key] → Sign Transaction
Oko:
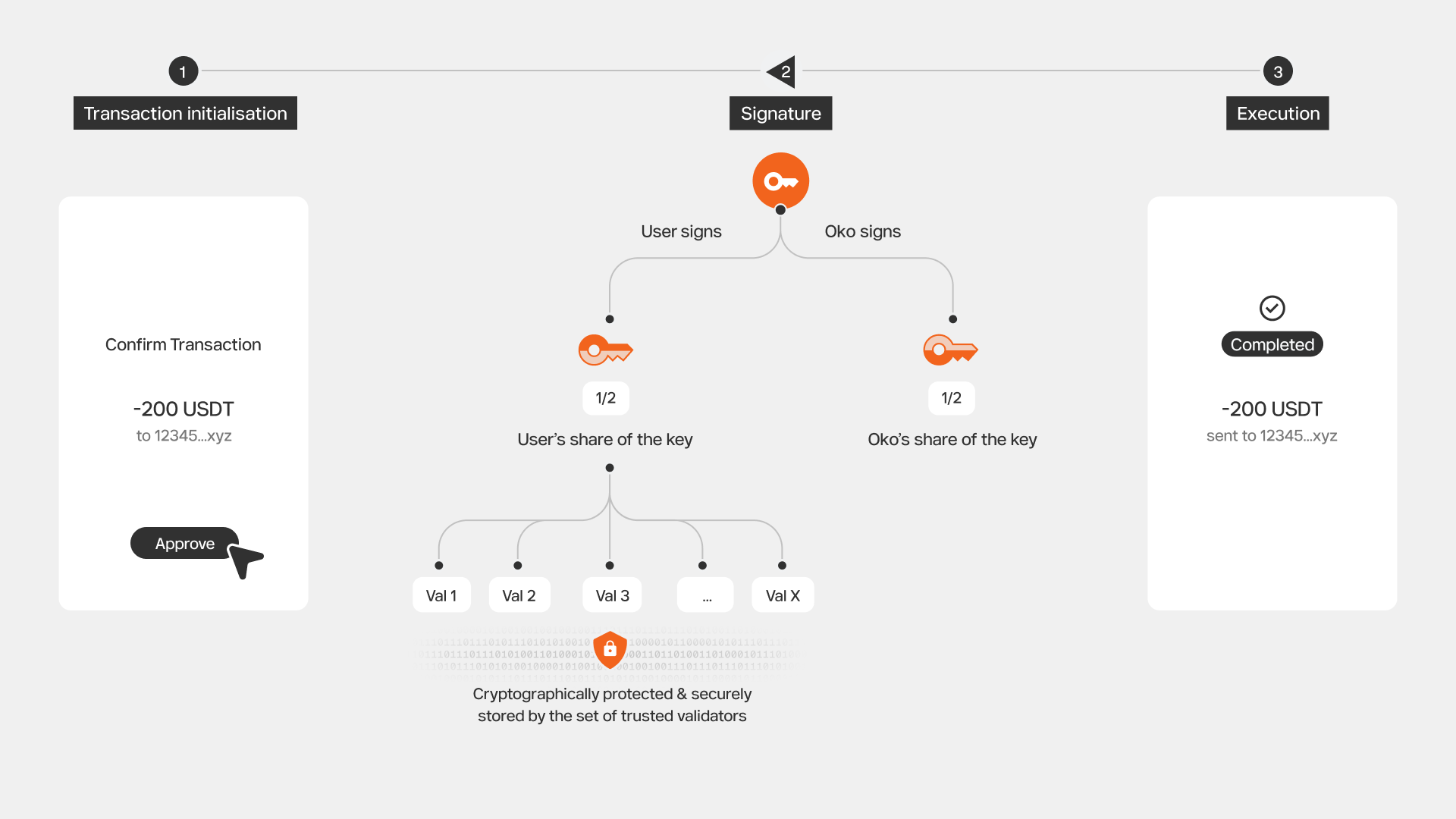
[Oko Key Share] + [User Key Share] → Sign Transaction
- One key is managed by Oko
- The user key is cryptographically protected and requires coordination from a decentralized validator set to enable signing
Key Share Lifecycle
Oko operates a 2-of-2 signing scheme where one key share stays with the Oko infrastructure while the other belongs to the end user. The user share is immediately split with Shamir Secret Sharing (SSS) and each fragment is stored on independent Key Share Nodes. When the user logs in, the client authenticates with each node (by presenting OAuth tokens) so the nodes can verify the user and release their encrypted fragments. The fragments are recombined exactly once during sign-in, remain on-device, and still represent only half of the full private key. For transaction signing, both key shares participate in a threshold signature protocol to produce a standard secp256k1 signature. See Threshold ECDSA Concepts for details on the signing process.
The master key (or private key) is never reconstructed or revealed at any point. This ensures users retain full control without compromising on security, while eliminating the need to manage complex private keys themselves.
Why This Matters for Your Integration
🔒 Enhanced Security for Your Users
- No single private key exists - mathematically impossible for one party to steal funds
- Distributed trust model - multiple parties must cooperate to authorize transactions
- Cryptographic guarantees - security backed by proven threshold signature protocols
🚀 Better User Experience
- No browser extensions - embedded directly in your application
- Google OAuth login - familiar authentication flow for mainstream users
- Cross-device compatibility - works on mobile, desktop, any browser
- Seamless onboarding - users don't need to learn about seed phrases or hardware wallets
⚡ Simple Integration
- Drop-in replacement - replace
window.ethereumwith Oko ethereum provider - Standard ECDSA signatures - compatible with all existing blockchain infrastructure
- Multi-chain support - Ethereum and Cosmos ecosystems
- Familiar APIs - uses EIP-1193 and CosmJS standards
Technical Implementation
Cryptographic Foundation
Protocol: Cait-Sith threshold ECDSA with committed Beaver triples
Implementation: Rust core with WebAssembly and Node.js bindings
Curve: secp256k1 (standard Bitcoin/Ethereum curve)
Standards: Full EIP-1193 and CosmJS compatibility
Integration Architecture
Your dApp
↓
Oko SDK
↓
Distributed Key Shares → Threshold Signature → Blockchain
For Ethereum:
import { OkoEthWallet } from "@oko-wallet/oko-sdk-eth";
import { createWalletClient, custom } from "viem";
// Initialize Oko Eth Wallet
const okoEthRes = OkoEthWallet.init({
api_key: "your-api-key",
});
if (!okoEthRes.success) {
throw new Error("Failed to initialize Oko Eth Wallet");
}
const okoEth = okoEthRes.data;
// Get provider
const provider = await okoEth.getEthereumProvider();
// Everything else stays the same
const walletClient = createWalletClient({
transport: custom(provider),
});
For Cosmos:
import { OkoCosmosWallet } from "@oko-wallet/oko-sdk-cosmos";
// Initialize Oko Cosmos Wallet
const okoCosmosRes = OkoCosmosWallet.init({
api_key: "your-api-key",
});
if (!okoCosmosRes.success) {
throw new Error("Failed to initialize Oko Cosmos Wallet");
}
const okoCosmos = okoCosmosRes.data;
// Get user accounts
const accounts = await okoCosmos.getAccounts();
Security Model
Isolation Boundaries:
- Wallet UI runs in secure iframe context
- Key shares stored in separate, encrypted databases
- Authentication handled through Google OAuth
Data Protection:
- No single private key ever exists
- Key material distributed across multiple parties
- All operations cryptographically auditable
Network Security:
- TLS encryption for all communications
- CORS and security headers
- JWT-based authentication
Competitive Advantages
vs. MetaMask/Browser Extensions
- Better Security: No single private key vulnerability
- Better UX: No extension installation required
- Cross-Platform: Works on mobile and desktop
vs. Custodial Wallets
- Better Security: Users maintain cryptographic control
- Better Privacy: No single entity can access funds
- Better Compliance: Distributed custody model
vs. MPC Wallets
- Proven Cryptography: Standard ECDSA signatures (not experimental)
- Better Integration: Drop-in replacement for existing wallet connections
- Better Scalability: Optimized threshold signature protocol
Ready to Integrate?
🚀 Quick Start:
Integration Guide - Add to your dApp
in minutes
📚 Examples: SDK Documentation - Copy-paste
code samples
🧩 Starter Templates:
Starter Templates - Ready-to-run
examples
🔍 Deep Dive: Threshold ECDSA Explained -
Understanding the cryptography